A liquid or a solution that conducts electricity
is called an electrolyte; solutions like copper sulphate, sodium chloride and
silver nitrate are common examples of electrolytes. When a current is passed
through an electrolyte, chemical action takes place and it is decomposed. This
is known as electrolysis.
The vessel in which electrolysis takes place is called a voltmeter. Two metal plates dipping in the electrolyte are called the
electrodes. The electrode through which current enters the electrolyte is
called the anode. The electrode through which current leaves the electrolyte is
called the cathode.
Water voltameter
Acidified water is electrolysed in a water voltameter with platinum
electrodes. Water is decomposed into hydrogen and oxygen. The electro-positive hydrogen
goes to the cathode and is evolved there as gaseous hydrogen. Electronegative
oxygen ion is collected at the anode.
Silver voltameter
Silver nitrate solution is an electrolyte in a silver voltameter
with silver electrodes. Silver is deposited on the cathode, and the oxide goes
into solution.
Copper voltameter
Copper sulphate solution is an electrolyte in a copper voltameter
with copper electrodes. Copper is deposited on the cathode.
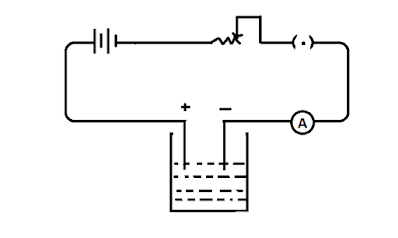
Determination of the chemical equivalent of copper
A copper voltameter consists of a glass vessel containing
copper sulphate solution. Tow copper plates which form the electrodes are kept
immersed in the solution. The plate connected to the positive of the battery is
called the anode and that connected to the negative of the battery is called
the cathode.
The copper voltameter is connected in series with a battery
and key. The circuit is closed and the rheostat is adjusted so that the ammeter
reads 1 ampere.
The current is then stopped. The cathode is removed, cleaned
well with sandpaper, washed and dried. Its weight correct to milligram is determined
by the method of vibrations. The weight plate is then replaced and the circuit
is closed.
A stopped clock is immediately started. The ammeter reading is
noted every 5 minutes. At the end of 30 minutes, the current is stopped. The cathode
is removed, rinsed in still water and dried. Its weight is accurately
determined.
Tags
science